Acceleration, Handling, and Efficiency: Electric Exotic Cars vs. Traditional Supercars
Introduction
The automotive industry is undergoing a significant transformation, particularly with the rise of electric vehicles (EVs). As concerns about climate change and fossil fuel dependency intensify, the shift towards electric mobility has gained momentum. This article explores various dimensions of electric vehicles, including their cost, affordability, performance, convenience, and charging accessibility. Understanding these aspects is essential for consumers considering making the switch to EVs, as well as for policymakers and industry stakeholders aiming to promote sustainable transportation solutions.
Cost of Electric Vehicles
Initial Purchase Price
The initial purchase price of electric vehicles has historically been higher than that of traditional gasoline-powered vehicles. Factors such as battery technology and production costs contribute to this price disparity. However, recent advancements in technology have begun to close the gap. Major manufacturers are progressively releasing more affordable models, making EVs accessible to a broader audience.
Despite the higher upfront cost, potential buyers should consider the total cost of ownership over the vehicle’s lifespan. As the market evolves, the prices of EVs are expected to decline further, making them even more competitive with internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles.
Long-Term Financial Benefits
While the initial investment in an electric vehicle may be higher, several long-term financial benefits make them an appealing choice. For starters, EVs typically have lower operating costs. Electricity is generally cheaper than gasoline, and electric motors are more efficient than traditional engines. This translates into significant savings at the pump for consumers who drive regularly.
Moreover, maintenance costs are often lower for electric vehicles. EVs have fewer moving parts and do not require oil changes, which reduces routine maintenance expenses. These long-term savings can offset the higher purchase price over time, making electric vehicles a financially sound investment.
Affordability
Government Incentives
To encourage the adoption of electric vehicles, many governments worldwide have implemented various incentives. These may include direct tax rebates, grants, and reduced registration fees. In some regions, buyers can receive significant financial assistance, which can substantially lower the effective purchase price of an EV.
In addition to direct financial incentives, some governments offer perks such as access to carpool lanes or exemptions from congestion charges, further enhancing the economic attractiveness of electric vehicles. Such incentives play a vital role in making EVs more affordable and appealing to consumers.
Financing Options
Another avenue to improve the affordability of electric vehicles is through financing options. Many financial institutions offer specialized loans for EV purchases, often with lower interest rates compared to conventional auto loans. These financing solutions can make the transition to electric vehicles more feasible for a larger segment of the population.
Furthermore, leasing options are becoming increasingly popular, allowing consumers to drive an electric vehicle without the burden of full ownership costs. These arrangements often include maintenance and charging benefits, reducing the overall financial commitment while providing an opportunity to experience the advantages of electric mobility.
Performance
Acceleration and Speed
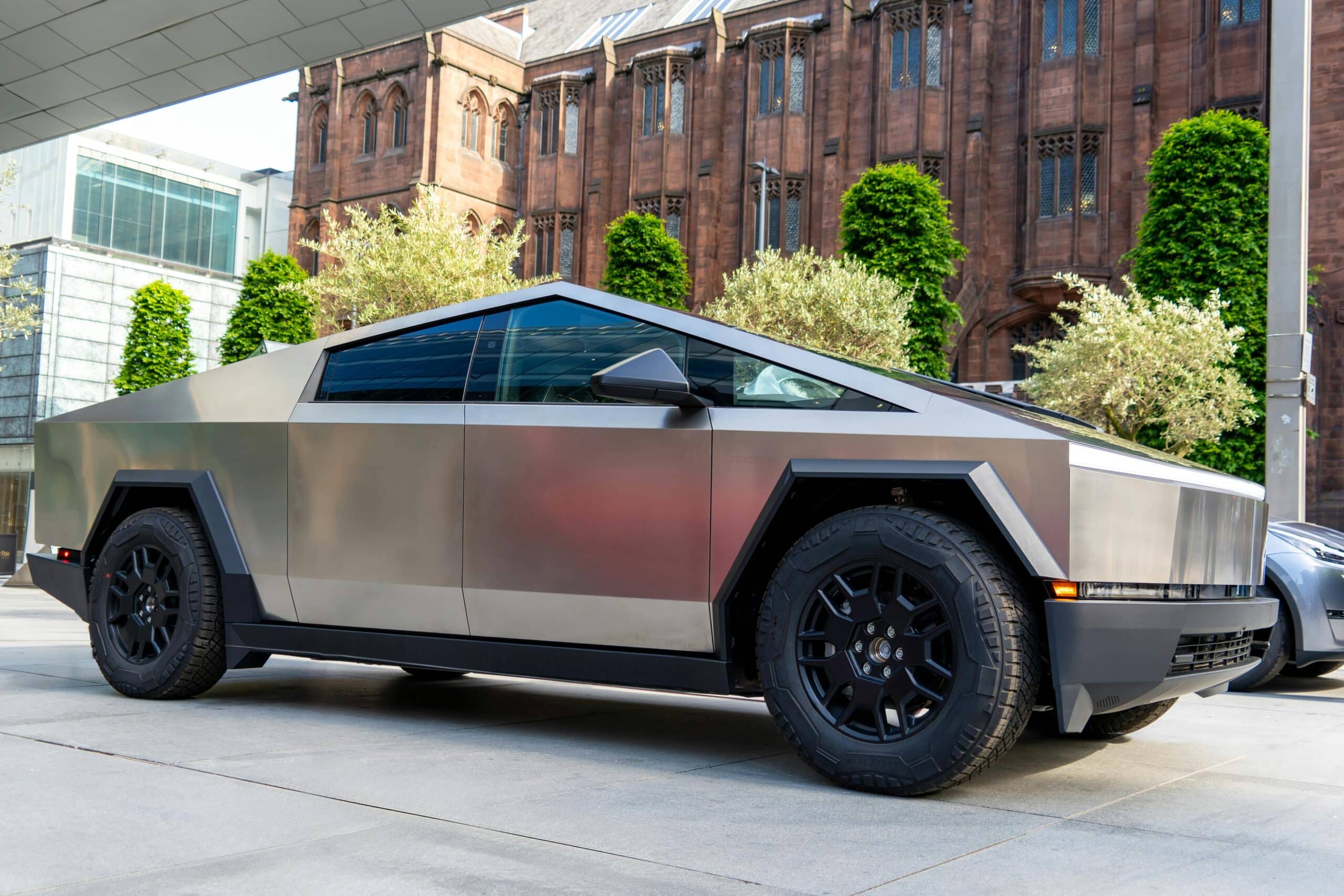
Electric vehicles are renowned for their impressive acceleration and speed. Unlike traditional engines, electric motors deliver maximum torque instantly, providing a thrilling driving experience. Many EV models can accelerate from 0 to 60 mph in a matter of seconds, rivaling even high-performance sports cars.
This rapid acceleration not only enhances the driving experience but also improves safety by allowing drivers to maneuver quickly in various traffic situations. As battery technology continues to advance, the performance capabilities of electric vehicles are expected to improve even further, making them an increasingly attractive option for enthusiasts and everyday drivers alike.
Driving Range
One of the primary concerns for potential electric vehicle buyers is the driving range. Early EV models often had limited range, causing range anxiety among consumers. However, recent advancements in battery technology have resulted in electric vehicles that can travel over 300 miles on a single charge, significantly alleviating these concerns.
As manufacturers invest in research and development, the driving range of electric vehicles is likely to continue increasing, making them suitable for longer trips and everyday commuting without the need for frequent recharging.
Maintenance Requirements
Maintaining an electric vehicle is generally simpler than maintaining a gas-powered vehicle. The fewer moving parts in an electric motor mean less wear and tear and fewer components that require regular servicing. For instance, EVs do not require oil changes, and brake wear is often minimal due to regenerative braking systems.
While there are still essential maintenance tasks—such as checking tire health and replacing brake pads—these are less frequent and often less expensive than the maintenance costs associated with traditional vehicles. This reduced maintenance burden makes EVs attractive for consumers looking to minimize long-term ownership costs.
Convenience
Daily Usability
Electric vehicles are increasingly designed with daily usability in mind. Many models offer spacious interiors, advanced technology features, and ample cargo space, making them suitable for a variety of lifestyles. Additionally, the quiet operation of electric vehicles enhances the driving experience in urban environments, providing a serene alternative to the noise of traditional combustion engines.
For city dwellers, the compact design of many electric models is advantageous, allowing for easier parking and maneuverability in congested areas. Their ability to provide instant torque and responsive handling ensures that electric vehicles are not only practical but also enjoyable to drive in day-to-day scenarios.
Integration with Smart Technology
The integration of smart technology in electric vehicles enhances convenience and user experience. Many modern EVs come equipped with advanced infotainment systems that support smartphone connectivity, navigation, and real-time traffic updates. This functionality allows drivers to maximize their time on the road and make informed decisions about their routes.
Moreover, some electric vehicles offer features such as remote start, smart charging schedules, and over-the-air software updates. This level of automation and connectivity not only adds to the convenience of owning an EV but also ensures that the vehicle can evolve with changing technology and user needs.
Charging Accessibility
Home Charging Solutions
Charging accessibility is a crucial factor in the widespread adoption of electric vehicles. For many owners, home charging solutions are the most convenient option. Installing a Level 2 charger in a residential garage allows drivers to charge their vehicles overnight, ensuring that they start each day with a full battery.
In addition to home charging stations, many municipalities offer incentives for homeowners to install charging infrastructure, further facilitating the transition to electric mobility. The convenience of home charging eliminates the need for regular trips to gas stations, making electric vehicles particularly appealing for those with a stable home base.
Public Charging Infrastructure
As the number of electric vehicles on the road increases, so does the need for accessible public charging infrastructure. Many cities and regions are investing in the development of charging networks, incorporating charging stations in public areas, shopping centers, and workplaces. This expansion makes it easier for EV owners to recharge their vehicles while running errands or at work.
Public charging stations typically offer Level 2 charging and, increasingly, DC fast charging capabilities. These fast chargers can replenish a significant portion of an EV’s battery in a short amount of time, alleviating range anxiety and making long-distance travel more feasible for electric vehicle owners.
Fast Charging Options
Fast charging technology is a game-changer for electric vehicle convenience. With the availability of DC fast chargers, EV owners can charge their vehicles to about 80% in as little as 30 minutes. These stations are strategically placed along major highways and travel routes, making long-distance travel much more practical.
As charging technology continues to evolve, the time it takes to charge an electric vehicle will likely decrease further. This innovation is crucial for boosting consumer confidence in EVs as a viable alternative to traditional vehicles, particularly for those who frequently embark on longer journeys.
Conclusion
The future of electric vehicles is bright, characterized by advancements in technology, affordability, and convenience. As consumers become increasingly conscious of their environmental impact, the shift towards electric mobility is gaining traction. While challenges remain, such as initial costs and charging infrastructure, the benefits of electric vehicles—including lower operating expenses, impressive performance, and integration with smart technology—make them an attractive option for a growing number of consumers.
As the automotive landscape continues to evolve, stakeholders must work collaboratively to address barriers to adoption, ensuring that electric vehicles become a mainstream solution for sustainable transportation. The ongoing transition to electric mobility promises not only to redefine the automotive industry but also to contribute positively to global efforts for a cleaner, more sustainable future.
FAQs
What is the average cost of an electric vehicle?
The average cost of an electric vehicle varies by model and manufacturer but typically ranges from $30,000 to over $100,000 for luxury models. Government incentives can significantly lower this cost.
How long does it take to charge an electric vehicle?
Charging time for electric vehicles can vary based on the charging method. Level 1 chargers (standard outlets) may take several hours, while Level 2 chargers could take 4-8 hours. DC fast chargers can recharge an EV to about 80% in approximately 30 minutes.
Are electric vehicles more environmentally friendly than gas vehicles?
Yes, electric vehicles produce zero tailpipe emissions, making them more environmentally friendly than gas vehicles. Their overall environmental impact also depends on the source of the electricity used for charging.
What are the typical maintenance costs for electric vehicles?
Electric vehicles generally have lower maintenance costs than gasoline vehicles, mainly due to fewer moving parts and no need for oil changes. Routine maintenance may include tire rotations and brake inspections but is less frequent overall.
Can I charge an electric vehicle at home?
Yes, most electric vehicle owners install Level 2 chargers at home for convenient overnight charging. Basic Level 1 charging is also possible using regular household outlets, though it is slower.
Add a comment Cancel reply
Comments (0)
Categories
- Uncategorized (10)
Recent Posts
About us

Related posts